The following relations describe monthly demand and supply conditions in the metropolitan area for recyclable aluminum.
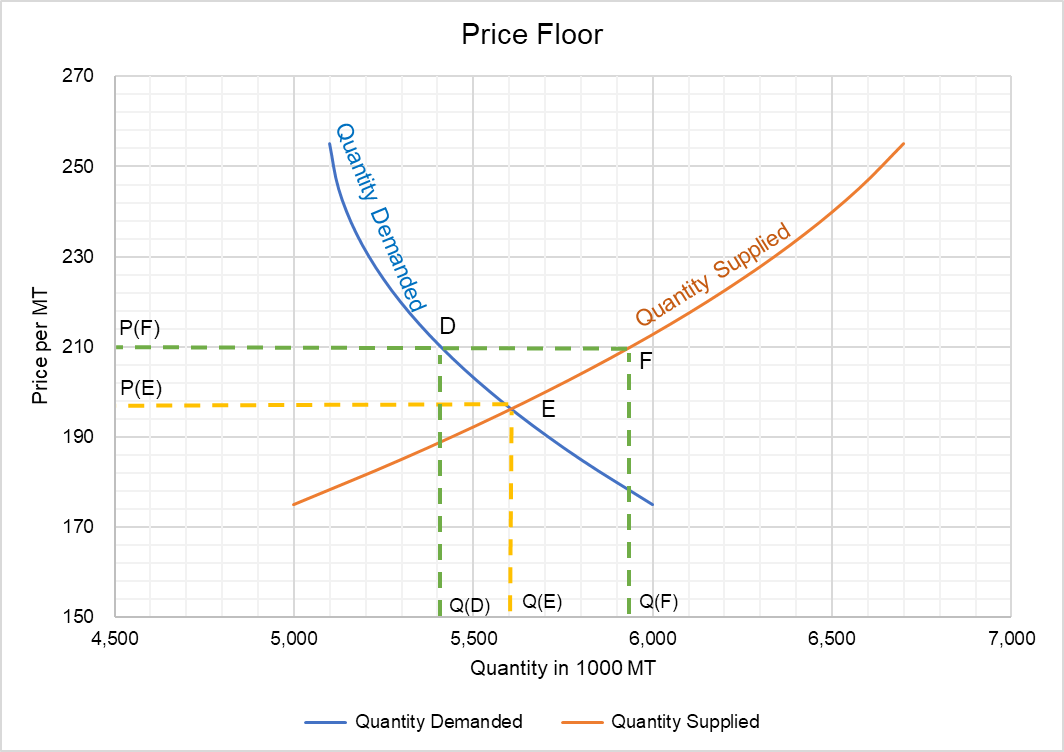
Demand and supply market equilibrium floor price.
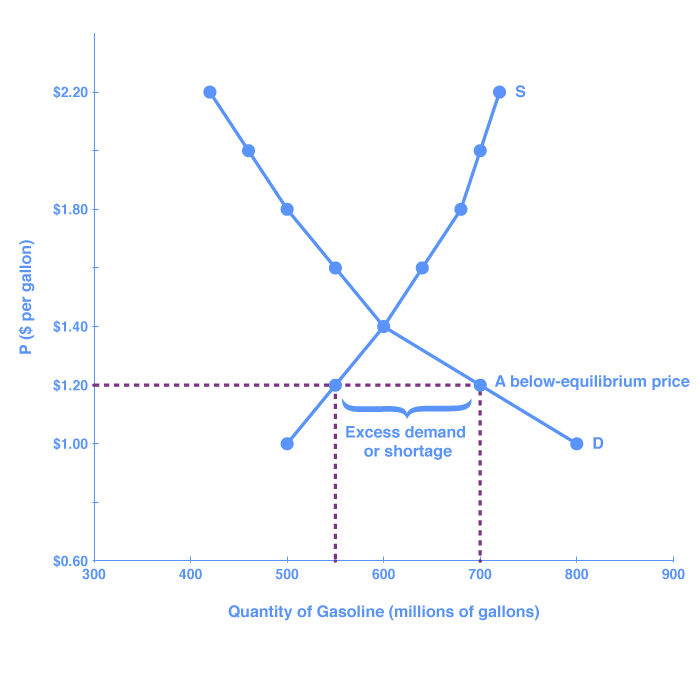
Now suppose that the price is below its equilibrium level at 1 20 per gallon as the dashed horizontal line at this price in figure 3 shows.
Demand supply consumer surplus market equilibrium price floor.
Q d 80 000 20 000p x demand.
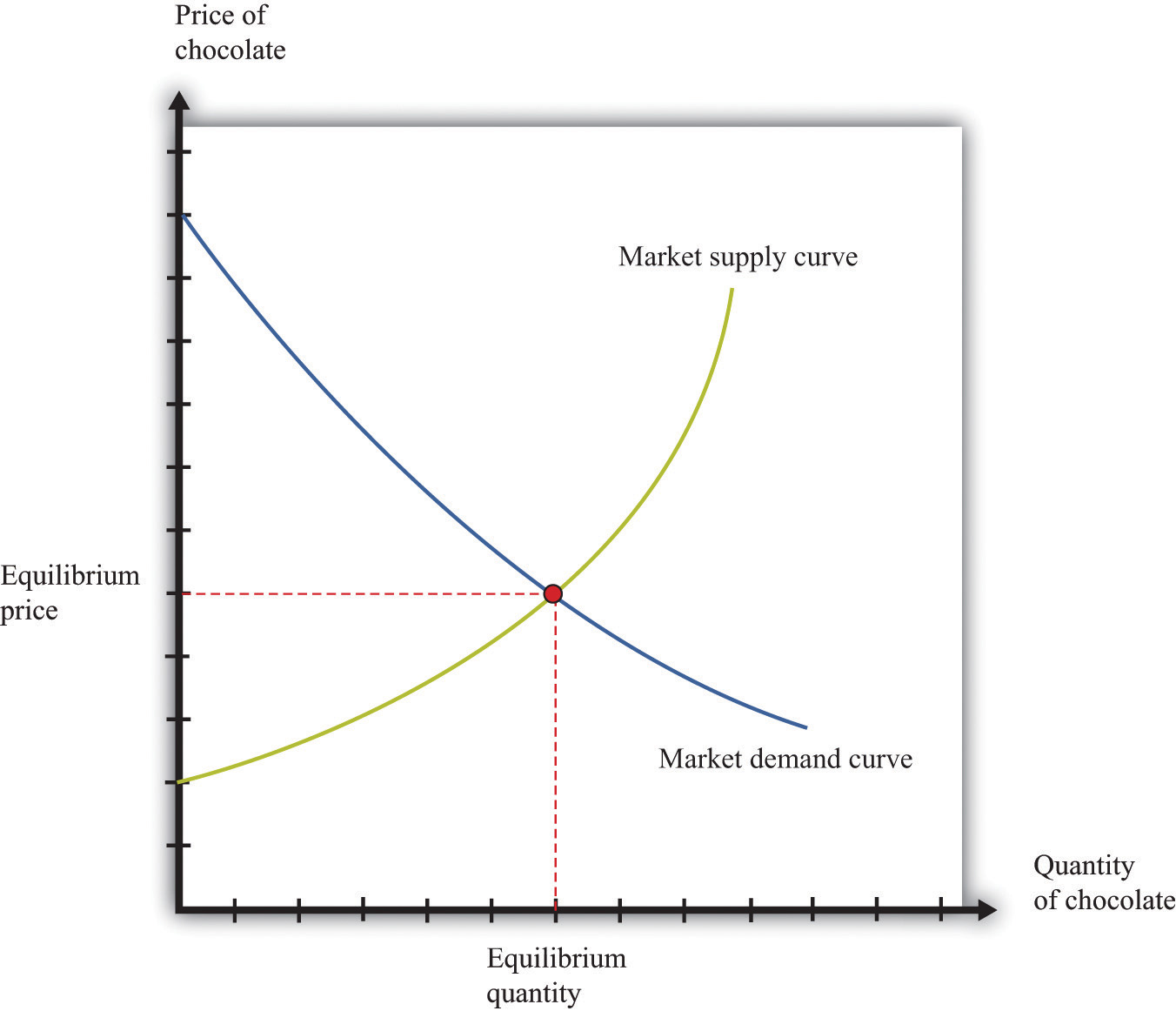
The equilibrium is located at the intersection of the curves.
A quick and comprehensive intro to supply and demand.
Market interventions and deadweight loss.
Neither price ceilings nor price floors cause demand or supply to change.
Taxes and perfectly elastic demand.
Rent control and deadweight loss.
A non binding price floor is one that is lower than the equilibrium market price.
Taxes and perfectly inelastic demand.
Minimum wage and price floors.
The equilibrium market price is p and the equilibrium market quantity is q.
A market demand curve plots the quantities of a product or service which consumers are willing and able to buy with reference to.
So if the price is above the equilibrium level incentives built into the structure of demand and supply will create pressures for the price to fall toward the equilibrium.
How price controls reallocate surplus.
The original intersection of demand and supply occurs at e 0 if demand shifts from d 0 to d 1 the new equilibrium would be at e 1 unless a price ceiling prevents the price from rising.
Remember changes in price do not cause demand or supply to change.
The equilibrium price of a product is determined when the forces of demand and supply meet.
Consider the figure below.
They simply set a price that limits what can be legally charged in the market.
We draw a demand and supply.
A price ceiling example rent control.
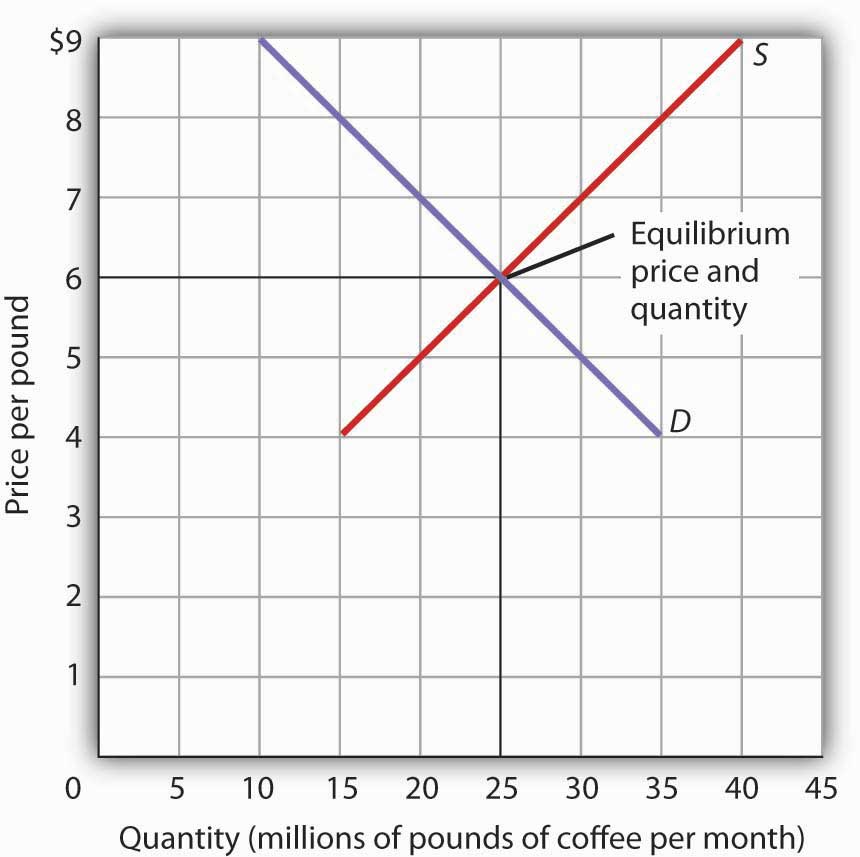
For understanding the determination of market equilibrium price let us take the example of talcum powder shown in table 10.
Dallas epperson cc by sa 3 0 creative commons.
Market clearing price is the price at which the quantity demanded of a product or service equals quantity supplied and no surplus or shortage exists in the market.
It is the price that corresponds to the point of intersection of the demand curve and the supply curve.
Even though the concepts of supply and demand are introduced separately it s the combination of these forces that determine how much of a good or service is produced and consumed in an economy and at what price.
Price ceilings and price floors.
Do price ceilings and floors change demand or supply.
If the price is not permitted to rise the quantity supplied remains at 15 000.
The government establishes a price floor of pf.
We define the demand curve supply curve and equilibrium price quantity.